In an ever-evolving landscape of risks and uncertainties, insurance companies face the pressing need to re-evaluate their value propositions to ensure long-term profitability and sustainability. As traditional models of insurance become increasingly challenged by emerging risks and changing consumer expectations, companies must adapt by expanding their coverage options and venturing into new markets.
The Need for Diversification
Insurance companies traditionally operate within well-defined sectors such as life, health, property, and casualty insurance. However, as the world becomes more interconnected and risks become more complex, the demand for specialized coverage is on the rise. From cyber threats to climate change-related perils, there’s a growing recognition that traditional insurance products may not adequately address modern risks.
Stagnant growth in mature markets and increasing competition have also compelled insurers to explore new avenues for revenue generation. Diversification offers insurance companies the opportunity to tap into underserved markets, differentiate themselves from competitors, and mitigate concentration risk.
Expanding Coverage Options
One of the most effective strategies for diversification is expanding coverage by developing innovative insurance products tailored to specific industries, professions, or lifestyle choices. Insurers can introduce policies covering cyber liability, reputation management, or even pandemics.
When certain policies do not cover an entire claim or casualty, there is opportunity to offer customers a marketplace of complementary services at lower prices to acquire substitute products. In this way, businesses can better serve customers while obtaining a new revenue stream.
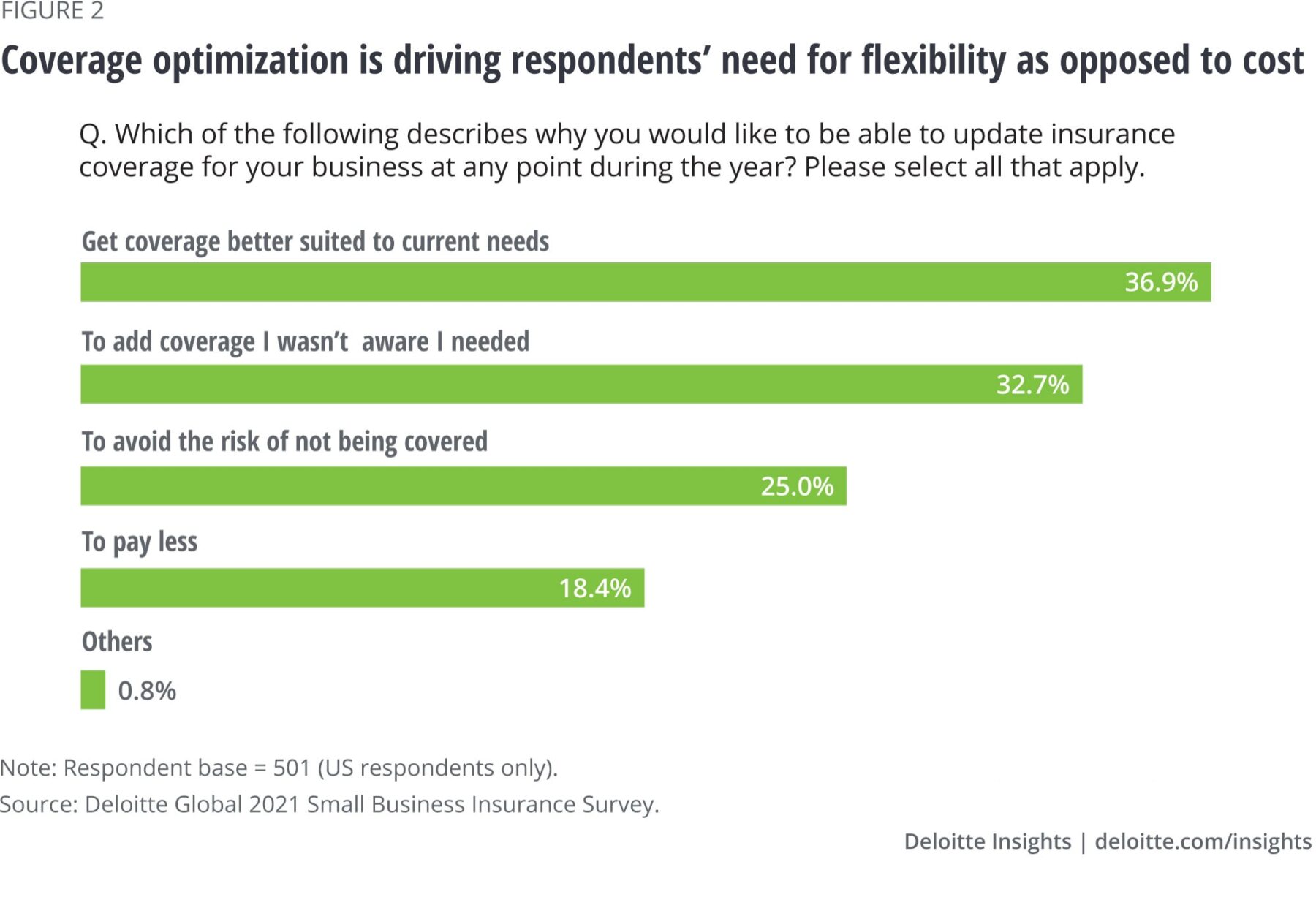
According to a recent Deloitte study, more business insurance customers are seeking greater levels of flexibility in their insurance products and policies. A significant portion express the desire to adjust coverage and premium rates periodically throughout the year, contingent upon business conditions. The traditional models of annual reviews and one-time coverage modifications are no longer considered viable.
The primary motivations behind desiring such flexibility do not revolve around cost reduction. Instead, respondents expressed a greater interest in optimizing their coverage. An example is having the ability to deactivate insurance coverage during periods of inactivity, such as with pay-as-you-go workers’ compensation policies. This approach enables adjustments to coverage when a company undergoes layoffs or experiences a seasonal downturn.
Entering New Markets
Expanding into new geographic markets or demographic segments offer immense growth potential, driven by rising incomes, urbanization, and increasing awareness about the importance of insurance protection in emerging economies.
Targeting underserved demographics such as millennials or gig economy workers can be lucrative, as these groups often have unique insurance needs and preferences, necessitating tailored products and distribution channels.
Insurance organizations should also look at rising trends within their markets, like electric vehicles and ride-sharing in the automotive industry, to assess opportunities for growth.These trending markets carry high avenues of expansion with possibly low competition.
Re-evaluating Value Propositions
In the quest for diversification, insurers must re-evaluate their value propositions to align with changing customer expectations. This involves emphasizing transparency, simplicity, and customer-centricity. Transparent pricing, devoid of hidden fees or complex terms, fosters trust and enhances the perceived value of insurance products.
Furthermore, educating customers about risk mitigation strategies is paramount in today’s risk-prone environment. Insurers can leverage digital platforms, interactive tools, and personalized advice to empower customers to proactively manage risks and reduce potential losses. By positioning themselves as risk management partners rather than just providers of financial protection, insurers can deepen customer engagement and loyalty.
Challenges and Considerations
Despite the opportunities presented by diversification, insurers must navigate several challenges. Regulatory compliance, cultural differences, and operational complexities can pose hurdles when entering new markets. Moreover, developing innovative products requires substantial investment in research, technology, and talent.
Insurers must strike a balance between diversification and maintaining underwriting discipline. Overextending into unfamiliar territories or offering overly complex products can expose insurers to undue risks and erode profitability.
Implementing Diversification
Expanding coverage options, entering new markets, and re-evaluating value propositions are key strategies for meeting the evolving needs of customers and securing future growth.
By embracing innovation and transparency, as well as prioritizing customer-centricity, insurers can differentiate themselves in a crowded marketplace and build a resilient business model capable of withstanding the challenges of tomorrow. In doing so, they not only safeguard their own profitability and sustainability but also contribute to the overall resilience of the societies they serve.
- Steve Millerhttps://epaypolicy.com/blog/author/steve-miller/
- Steve Millerhttps://epaypolicy.com/blog/author/steve-miller/
- Steve Millerhttps://epaypolicy.com/blog/author/steve-miller/
- Steve Millerhttps://epaypolicy.com/blog/author/steve-miller/




